Angle-closure glaucoma (ACG) is a sight-threatening eye condition that arises from the obstruction of the drainage angle within the eye, leading to a rapid increase in intraocular pressure (IOP). Unlike open-angle glaucoma, angle-closure glaucoma manifests with sudden and severe symptoms, making timely intervention crucial. In this article, we will explore the characteristics, risk factors, and urgency associated with angle-closure glaucoma.

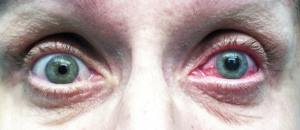
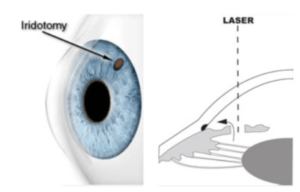
LPI is a laser procedure that creates a small hole in the peripheral iris, allowing the aqueous humor to flow more freely and relieve the blockage at the drainage angle. This procedure is often performed urgently to addreccthe underlying cause.
Angle-closure glaucoma demands swift and decisive action due to its sudden onset and potential for rapid vision loss. Recognizing the symptoms, understanding the risk factors, and seeking immediate medical attention are crucial for a favorable outcome. Regular eye examinations, especially for individuals at higher risk, play a preventive role in identifying anatomical predispositions and allowing for proactive management. Remember, when it comes to angle-closure glaucoma, time is of the essence, and prompt intervention can make a significant difference in preserving vision and preventing long-term complications.